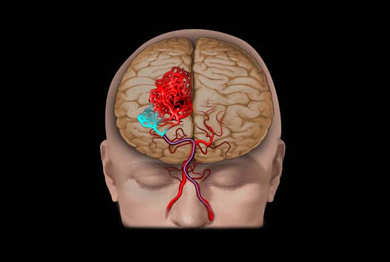
 Arteriovenous malformations are abnormal clusters of blood vessels which can be seen in any part of the human body. They are congenital in nature. In he brain ,AVM’s may have no symptoms at all and the abnormality may be picked during a brain scan for another reason. However , one the commonest presentations is with a bleed in the brain resulting in paralysis or unconsciousness. Another form of presentation can be seizures. Its also known that AVM,s can at time’s result in frequent head aches termed “vascular headaches”. When detected, AVMs are ideally treated to prevent bleeding in future.
Arteriovenous malformations are abnormal clusters of blood vessels which can be seen in any part of the human body. They are congenital in nature. In he brain ,AVM’s may have no symptoms at all and the abnormality may be picked during a brain scan for another reason. However , one the commonest presentations is with a bleed in the brain resulting in paralysis or unconsciousness. Another form of presentation can be seizures. Its also known that AVM,s can at time’s result in frequent head aches termed “vascular headaches”. When detected, AVMs are ideally treated to prevent bleeding in future.
Procedure Details
Patients with AVM’s may have no symptoms at all and the abnormality may be picked during a brain scan for another reason. However one the commonest presentations is with a bleed in the brain resulting in paralysis or unconsciousness . Another form of presentation can be seizures . Its also known that AVM,s can a time result in frequent head aches termed “vascular headaches”.
Diagnosis :
The Diagnosis or a vascular malformation is usually made on CT or MR. However, Angiography is a mandatory investigation to not only confirm the diagnosis but to also understand the character and morphology of the malformation . Its also important to measure the size of the AVM since the management would depend on this.
Treatment options:
The three options that are available in the management of AVM’S are
- open surgery
- endovascular therapy
- radio surgery.
Often multiple modalities have to be used to cure an AVM.
Open surgery :
Open surgery is reserved for large AVM’S .However, it is a risky procedure and has to be performed by surgeons specially trained to do these procedures . Here, the skull is opened and the malformation located and the abnormal cluster of vessels delicately excised.
Endovascular(embolization) therapy:
 Endovascular(embolization) therapy is performed like Angiography .through a small skin puncture a catheter is navigated under imaging control and placed in the blood vessel that supplies the region of the brain that has the AVM. Another thinner and softer tube is then navigated right up to the AVM and a special medical glue “onyx” is then slowly injected to fill abnormal spaces in the vascular malformation . This procedure may have to done in two three sittings if it is large smaller AVM’s can be treated in one sitting.
Endovascular(embolization) therapy is performed like Angiography .through a small skin puncture a catheter is navigated under imaging control and placed in the blood vessel that supplies the region of the brain that has the AVM. Another thinner and softer tube is then navigated right up to the AVM and a special medical glue “onyx” is then slowly injected to fill abnormal spaces in the vascular malformation . This procedure may have to done in two three sittings if it is large smaller AVM’s can be treated in one sitting.
Stereo-tactic radio-surgery :
Stereo-tactic radio-surgery is another form of treatment which is used in small AVM’s especially when the risk of bleeding is low. Although the term surgery is used the procedure involves no surgery at all. The treatment is a highly specialized form of radiotherapy where multiple beams are focused on a single point . It is a procedure that describes accurate, precise delivery of ionizing radiation in a single fraction to an intra-cranial lesion with the intent of eradicating or stabilizing the focus of disease. SRS may be a viable alternative to conventional surgery for brain lesions such as brain mets, Arteriovenous Malformations (AVM), Gliobastoma Multiforme (GBM), Meningioma and Acoustic Neuroma (AN). However after this procedure it may take months to years before the AVM is finally obliterated and thus may not play a role when the AVM has a very high chance of bleeding.
Complications of Embolization :
Even though this procedure is safer than open surgery the following complications are possible – rupture of the AVM during embolization, clot formation in a normal blood vessel during the procedure or glue occluding a normal vessel. All these can lead to permanent disability or may even prove fatal.
