 The brain receives its blood supply from two sets of blood vessels,the Carotids in the front, and the Vertebral arteries at the back. If any of these vessels become narrow, then the patient may experience a condition termed TIA. In TIA one may experience a transient loss of consciousness , weakness in the limb.or blurring of vision. Narrowing of these vessels are generally caused by deposition of fat and fibrous tissue due to atherosclerosis. It can also be rarely seen due to inflammation of the blood vessels or arteritis. Till recently these patients had open surgery as the only option. However thanks to interventional radiology this narrow segment in the vessel can be safely opened through a small skin puncture by a procedure cord carotid / vertebral angioplasty and stenting.
The brain receives its blood supply from two sets of blood vessels,the Carotids in the front, and the Vertebral arteries at the back. If any of these vessels become narrow, then the patient may experience a condition termed TIA. In TIA one may experience a transient loss of consciousness , weakness in the limb.or blurring of vision. Narrowing of these vessels are generally caused by deposition of fat and fibrous tissue due to atherosclerosis. It can also be rarely seen due to inflammation of the blood vessels or arteritis. Till recently these patients had open surgery as the only option. However thanks to interventional radiology this narrow segment in the vessel can be safely opened through a small skin puncture by a procedure cord carotid / vertebral angioplasty and stenting.
Procedures Details
The brain can be considered to be the most vital organ of the body. Unlike any other organ the brain requires a continuous supply of blood. Severe damage can take place if this organ does not have oxygen for more than a few minutes.
One of the common causes of stroke is a occlusion of a blood vessel supplying a vital part of the brain. They are commonly caused by a small blood clot that develops at the site of narrowing in the carotid or vertebral arteries, which are the main blood vessels that supply the brain. the clot then detaches it self and migrates into the smaller intracranial vessels along the direction of flow.
Narrowing of these vessels are commonly caused by atherosclerosis. In this condition deposition of fat and fibrous tissue results in reduction in size of the lumen which in turn produces turbulence of blood across this segment. Another reason a blood vessel can be narrow is secondary to a type of inflammation called arteritis. This is commonly seen in young women.
Often carotid stenosis may have no symptoms at all and may be detected during a Doppler ultrasound of the neck. At times the patient may experience intermittent numbness or weakness of one half of the body or of a single extremity. Patients also may experience blurring or blindness in one eye which may last for a few seconds. This condition is called TIA.
Color Doppler evaluation of the neck vessels is a simple and accurate way to establish the diagnosis of carotid stenosis. Once this diagnosis is made, the patient should ideally receive treatment which could either be surgical or a non- surgical -carotid stentingand if the stenosis is more than 65%.
Technique
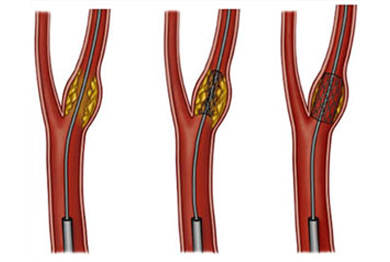 Carotid stenting involves taking a fine tube [catheter] under imaging guidance through small puncture in the blood vessel of the thigh into the suspected blood vessel that supplies the brain. This is performed under sophisticated imaging guidance. An angiogram is performed to confirm the diagnosis that is made by Doppler.
Carotid stenting involves taking a fine tube [catheter] under imaging guidance through small puncture in the blood vessel of the thigh into the suspected blood vessel that supplies the brain. This is performed under sophisticated imaging guidance. An angiogram is performed to confirm the diagnosis that is made by Doppler.
After this a fine wire which has a specialized medical filter is navigated across the narrow segment and placed beyond it in the normal vessel. The narrow segment is then dilated with a balloon catheter. The balloon is then exchanged for a fine metalmesh (stent). Further balloon dilatation is performed if the lumen continues to be narrow after stenting. Following the procedure the filter is captured in a specialized tube and removed. The puncture site in the groin is then compressed till hemostasis is achieved or an Angio-Seal device is used to prevent further bleeding.
There is enough evidence in the literature to conclusively said that carotid stenting is in no way inferior to open surgery for carotid stenosis.
Narrowing of the vertebral artery can also be treated in the same way. Here, unlike carotid stenting interventional radiology is the only way reestablished normal flow. Surgery of the vertebral arteries is difficult and dangerous.