About the Procedure
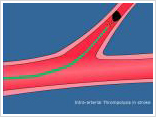
Because the brain relies on only two sets of major arteries for its blood supply, it is very important that these arteries are healthy. Then one of these blood vessels or its branches are suddenly blocked the brain tissue in that area stops functioning. If this block can be removed within the first 6 hours then, most of this tissue can be salvaged and the patient may have full recovery. It is not only important to remove this block but it is also mandate lead to ascertain the cause of this block. Sometimes narrowing in the blood vessel that leads to the brain [stenosis] can be the underlying reason for this block. Since stenotic segments are prone to generate blood clots which can then flow into the cerebral circulation leading to stroke. Today thanks to interventional radiology techniques a small catheter can be navigated right into the block and special proximal injected to dissolve and salvage the dying brain tissue. Further, the narrowing in the blood vessels can also be treated by angioplasty and stenting.
Procedures Details
“Brain Attack” is another name of Stroke:
The brain is the most important organ in the body. It cannot last for more than a few minutes without blood supply unlike any other organ in the body once the brain tissue dies one cannot do a procedure like a transplant to get back its normal function. Thus it is extremely important to recognize the warning signs of stroke and also to treat stroke at the earliest in the center that is it equipped to handle stroke.
WARNING SIGNS
There are also “warning signs” of an impending ischemic stroke, and stroke often does not strike unannounced.
PRIOR STROKE
– Stroke can strike a person twice. Suffering one stroke, regardless of its severity increases your chances of suffering a second stroke.
TIA (Transient Ischemic Attack)
– A TIA is a temporary Cerebrovascular disruption that leaves no permanent damage. These are recognizable events and can be predictor of a future, more devastating stroke. One of the common causes of TIA is narrowing of the blood vessel that supplies the brain it can either be in the vertebral or carotid artery. Of the two carotid stenosis is commoner.
CAROTID STENOSIS :
Carotid artery disease refers to plaque building up on the artery wall. The body’s natural reaction is to heal over it – much like a scab forming over a cut. This condition is called arteriosclerosis – artheroma is the plaque material that builds up, and sclerosis refers to the body’s reaction to harden the material. The material accumulates and narrows the artery. The narrowing is referred to as stenosis
Certain features of stenosis – such as the size of the artery and location of the blockage, or certain medical conditions in your history may call for different treatment called carotid Stenting. In this procedure, a small tube –like support called stent is threaded in to the narrowing artery from a hole made in the groin(in the same way the angiography catheter is inserted). The stent is then expanded and opens the narrowing, restoring normal blood supply to the brain. Today carotid stenting is a safe procedure especially if it is performed by placing a small filter in the blood vessel prior to stenting following the procedure this filter was removed. There is enough evidence to suggest that carotid stenting with filter protection is as safe as open surgery.
SYMPTOMS OF STROKE :
The single most important factor in treating an acute stroke is time. Stroke is an emergency. Stroke victims need urgent medical care. Symptoms of Ischemic stroke include:
VISUAL DISTURBANCES, INCLUDING BLOCKED OR LOSS OF VISION IN ONE EYE, BLURRY VISION OR “GRAYING”
“It seemed like someone was pulling a shade over one of my eyes”
WEAKNESS, NUMBNESS OR CLUMSINESS IN ONE ARM OR HAND OR LEG.
“My arm wouldn’t do what I wanted it to do”
“I couldn’t hold on to my coffee cup”
“I couldn’t lift up my arm/leg.”
“My arm felt tingly”
LANGUAGE PROBLEMS, INCLUDING SLURRED SPEECH
“I just couldn’t say anything”
“She sounded drunk”
“My family couldn’t make sense of what I was saying”
FACIAL DROOP/WEAKNESS
“The left side of my face was sagging”
DIZZINESS, STUMBLING
“I couldn’t walk straight”
Symptoms of Hemorrhagic Stroke include:
SEVERE OR SUDDEN HEADACHE
“I have the worst headache of my life”
LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS AND/OR VOMITING
If there is any doubt whether you, or someone around you, is experiencing a stroke, seek immediate medical attention.
TREATMENT OF ISCHEAMIC STROKE :
A thrombotic stroke occurs when a build up of plaque and blood clot, called a thrombus, blocks an artery to the brain and stops blood flow. An embolic stoke occurs when a piece of plaque or thrombus travels from its original site and blocks an artery down stream. The material that has moved is called an “embolus”. How much of the brain is damaged or effected depends on exactly how far downstream in the artery the blockage occurs.
EARLY TREATMENT CAN SAVE LIFE AND RESCUE THE BRAIN
There are new treatments available to help rescue cells in the first 6 hours, we can treat stroke and stop permanent brain damage by giving a clot dissolving drug intra-venously in the first 3 hours (TPA) or actually taking a small tube from the brain into the blocked blood vessel and we can dissolve the clot with drugs like urokinase within 3 to 6 hours of stroke. However, before drug therapies can be given, a CT scan must be obtained to rule out any bleeding in the brain. This takes precious time. The sooner you get to the hospital, the better chance you have for a good outcome.
All stroke victims must come in time to the hospital to make them eligible for this therapy which will make the difference between complete recovery and permanent disability.