About the Procedure
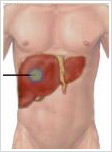
The word cancer has always been associated with pain, major surgeries, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and the many associated side effects. Thus scientist have always been in the lookout for newer treatment modalities that can make the treatment of cancer simple and easier . Radiofrequency ablation is one such treatment option which can help reduce the pain and side effects associated with cancer therapy.
Procedures Details
When Radiofrequency is applied to the tissue through a needle that is placed within it induces death of the cells secondary to the heat that is generated. Thus when a radiofrequency probe is placed within a tumor the tissue within the tumor dies. This is exactly what would have been if you can surgically removed the tumor. In addition, when the size of the tumor is small then a small area of normal surrounding tissue will also die reducing the chances of tumor spread. Each needle has the capacity of destroying tissue within a radius of 1.5 cm all around the needle. When the tumor is larger the number of needles used simultaneously destroy the tumor will increase. However, systems today do not have the ability of placing more than 3 needles at the given time thus it is believed that a tumor more than 5 cm is not ideally suitable for radiofrequency ablation.
Since and needle only destroys a target volume of tumor tissue by local heat there hardly any side effects compared to those associated with chemotherapy or radiotherapy. In addition a patient’s tolerance to the procedure is also high since the procedure is minimally invasive. The procedure requires the patient to stay in the hospital only for a few hours.
Most radiofrequency ablations are performed under general anesthesia not because the procedure is painful but to ensure that the patient lies still during placement of the needle. The needle is generally placed under CT guidance. Following the procedure the needle is removed and follow up CT scans are performed at the end of one-month, 3 months and 6 months.
The common areas where radiofrequency ablation has proved its use is in the management of cancer in the liver (both primary and secondary)., primary cancer of the kidney (when the tumor sizes less than 3 cm) , it is found use in the management of secondaries in the bone and also for a painful benign tumor of the bones called osteo-osteoma.
Radiofrequency ablation can also be used at times to reduce the size of inoperable tumors in the lungs.