Department of Endocrinology
We at endocrinology department treat diseases affecting the metabolism of the human body. Glands secretes hormones that have effects on the way the body appears, acts, and maintains itself. Endocrine diseases are manifested due to hormonal over-activity or under-activity or due to tumors.
Patients are often referred for treatment and evaluation of Hyperthyroidism (overactive Thyroid gland), Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid gland) and Thyroid cancer. We also treat diseases of the Pituitary such as Acromegaly (which is excessive production of Growth hormone), Cushings Syndrome (Excess production of Cortisol), Diabetes mellitus or excess production of Prolactin, various disruptions of Gonadal hormones (e.g. excess hair in women, breast development in men, arrested puberty, polycystic ovary syndrome, amenorrhea), bone disease (such as osteoporosis, rickets and hyperparathyroidism), diseases of the adrenal glands etc.
Dynamic Hormonal Testing
- Hormones are secreted at specific times from different glands in our body. In most cases a random sample of blood will be enough to make a diagnosis in addition to clinical examination and other investigations. We use state of art equipments such as fully automated analysers to provide us with real time results.
- In some instances inducing stress under controlled conditions with other hormones or drugs is a necessity. We have trained paramedical staff who can organize this at our center under the supervision of our consultants.
Outpatient procedures
- Fine needle aspiration of the thyroid is routinely done in our center to assess nodules in the Thyroid.
- Doppler assessment and biothesiometry can be done to assess peripheral vascular disease and neuropathy in diabetic patients.
- We administer Depot injections for conditions like precocious puberty, osteoporosis and testosterone replacement.
Dietary services
Our goal is to coach you to gain optimum nutrition pertaining to your clinical condition. We have dieticians working with us who will be able to advise you on individualised nutritional plans.
ENDOCRINOLOGY
What is Endocrinology?
Endocrinology is a branch of medicine dealing with the endocrine system. The endocrine system is a complex group of glands that make different hormones. Hormones are substances that help to control various activities in your body such as metabolism (food burning and waste elimination), growth, development and reproduction. Hormones also control the way you respond to your surroundings and they help to provide proper amount of energy and nutrition your body needs to function.
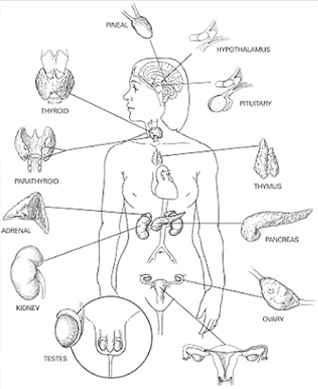
The most important glands that make up the endocrine system include the thyroid, parathyroid, pancreas, ovaries, testes, adrenal, pituitary and hypothalamus.
History
In the original 1902 definition by Bayliss and Starling, they specified that to be classified as a hormone, a chemical must be produced by an organ or gland, be released (in small amounts) into the blood and then transported by blood to a distant organ to exert its specific function. This definition holds true for most "classical" hormones, but there are also paracrine mechanisms (chemical communication between cells within a tissue or organ), autocrine signals (a chemical that acts on the same cell) and intracrine signals (a chemical that acts within the same cell).
Endocrinology as a profession
- An endocrinologist is a specially trained doctor. Your primary care doctor refers you to an endocrinologist when you have a problem with your endocrine system such as Hyperthyroidism, or Hypothyroidism and diabetes.
- Endocrinologists also treat patients who are overweight or obese, because of metabolic and hormonal problems. Thyroid, adrenal, ovarian,pancreatic and pituitary disorders can cause obesity. Endocrinologists also identify factors linked with obesity such as insulin resistance and genetic problems.
- Endocrinologists also conduct research to learn how the glands work and learn the best methods to treat patients with a hormone imbalance.
Work
The medical specialty of endocrinology involves the diagnostic evaluation of a wide variety of symptoms and variations and the long-term management of disorders of deficiency or excess of one or more hormones. Most endocrine disorders are chronic diseases that need life-long care.
The diagnosis and treatment of endocrine diseases are guided by laboratory tests to a greater extent than for most specialties. Many diseases are investigated through excitation/stimulation or inhibition/suppression testing. This might involve injection with a stimulating agent to test the function of an endocrine organ. Blood is then sampled to assess the changes of the relevant hormones or metabolites. An endocrinologist needs extensive knowledge of clinical chemistry and biochemistry to understand the uses and limitations of the investigations.
A second important aspect of the practice of endocrinology is distinguishing human variation from disease. Atypical patterns of physical development and abnormal test results must be put together to come to a definite diagnosis. Diagnostic imaging of endocrine organs may reveal incidental findings called incidentalomas, which may or may not represent disease. Its our task to judge the clinical importance of such tumors and then suggest a management plan.